Protocols

Protocols


FOREIGN BODIES IN ENT & GIT
Patients with foreign bodies (FB)in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract commonly present to the emergency department (ED).

FITTING
Symptoms that suggest a seizure include loss of consciousness, muscle spasms that shake the body, loss of bladder control, sudden confusion, and inability to pay attention

FEBRILE NEUTROPENIC OR CONCOLOGY PATIENTS
Antifungal agents can be withheld in a specific subset of high-risk febrile neutropenic patients. These patients include those who remain febrile after 4-7 days of broad-spectrum antibiotics but are clinically stable and without clinical or radiographic signs of fungal infection.

FEBRILE CONVULSIONS
Febrile seizures are convulsions that can happen during a fever (febrile means "feverish"). They affect kids 3 months to 6 years old, and are most common in toddlers 12–18 months old. The seizures usually last for a few minutes and are accompanied by a fever above 100.4°F (38°C).

FEBRILE CHILDREN
The mainstay of diagnosis is physical examination by a physician who is experienced in the care of children and adolescents.

EPISTAXIS
Epistaxis also called acute hemorrhage or nose bleed is a medical condition in which bleeding occurs from the nasal cavity of the nostril. Nose bleed can occur due to a trauma to the nose, due to accident, or injury to the interior of the nose from pricking.

ELECTROCUTION
Electrocution is death or serious injury caused by electric shock, electric current passing through the body.

ECLAMPSIA
a condition in which one or more convulsions occur in a pregnant woman suffering from high blood pressure, often followed by coma and posing a threat to the health of mother and baby.

ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg attaches itself in a place other than inside the uterus. Almost all ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube and are thus sometimes called tubal pregnancies

DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a dangerous complication faced by people with diabetes which happens when the body starts running out of insulin. DKA is most commonly associated with type 1 diabetes, however, people with type 2 diabetes that produce very little of their own insulin may also be affected.

DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but also can occur with no symptoms.
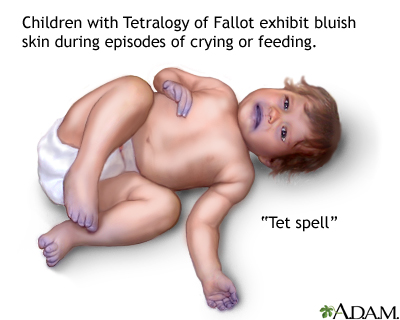
CYANOTIC EPISODE IN A CHILD
Cyanotic episodes spells. Cyanotic spells occur in children with cyanotic congenital heart disease, in particular tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary atresia. They usually occur early in the morning, or in the context of stress or dehydration ie. periods of increased oxygen demand/ultilisation.




